|
Overview
A properly functioning heel is essential to normal, smooth, and painless gait. The heel is the first area to strike the ground during normal gait, which means it takes the brunt of the stress incurred during walking and running activities. Of course, this also means that the heel is highly prone to injury. One such injury is called heel bursitis. Causes Bursitis has many causes, including autoimmune disorders, crystal deposition (gout and pseudogout), infectious diseases, traumatic events, and hemorrhagic disorders, as well as being secondary to overuse. Repetitive injury within the bursa results in local vasodilatation and increased vascular permeability, which stimulate the inflammatory cascade. Symptoms Medical experts strongly recommend that you consult a doctor if you have any of the symptoms below. Disabling joint pain that prevents you from doing your daily activities. Pain that lasts for more than two weeks. Excessive swelling, redness, bruising or a rash around the painful joint. Sharp or shooting pain, especially when you exercise or do something more strenuous. A fever. Any of the above could be a sign of infection, a condition such as arthritis or a more serious injury such as a tendon tear that may require medical attention. Diagnosis Before making a diagnosis of retrocalcaneal bursitis, a doctor must rule out other possible problems, such as arthritis, a fracture or tumor. A doctor also will try to determine if the Achilles tendon itself is a source of pain. To make a diagnosis, a doctor will use some or all of the diagnostic tools below Patient interview. A doctor will ask a patient about medical history, and to describe the onset of his or her symptoms, the pattern of pain and swelling, and how symptoms affect lifestyle. For example, doctors may ask patients what types of shoes they wear and what they do for exercise. A patient's reported symptoms are important to diagnosis and treatment. The doctor will also ask what home treatments have helped the condition. Physical exam. A doctor will examine the patient's foot, noting swelling, tenderness and pain points, and range of motion. The doctor also may ask the patient to point and flex the feet and stand on his or her toes. Non Surgical Treatment Caregivers may give you special shoe inserts with a cutout around the tender area. You may also be told to wear shoes with a reinforced heel counter. This will give better heel control. You may need other shoe inserts (wedges) to raise your heel so it does not press against the back of the shoe. You may also wear shoes that are open in the back, such as sandals that have no strap across the heel. You may use ibuprofen (eye-bu-PROH-fen) and acetaminophen (a-seet-a-MIN-oh-fen) medicine for your pain. These may be bought over-the-counter at drug or grocery stores. Do not take ibuprofen if you are allergic to aspirin. You may be given shots of medicine called steroids (STER-oids) to decrease inflammation. Caregivers may add local anesthesia (an-es-THEE-zah) to the steroids. This medicine helps decrease bursitis pain. Because these shots decrease swelling and pain, you may feel like your ankle is healed and that you can return to heavy exercise. It is important to not exercise until your caregiver says it is OK. You could make the bursitis worse if you exercise too soon. You may need surgery to remove the bursa or part of your ankle bone. Surgery is usually not necessary unless the bursitis is very bad and does not heal with other treatments. Your caregiver may want you to go to physical (FIZ-i-kal) therapy (THER-ah-pee). Physical therapists may use ultrasound to increase blood flow to the injured area. Caregivers may use massage to stretch the tissue and bring heat to the injury to increase blood flow. These and other treatments may help the bursitis heal faster. Exercises to stretch your Achilles tendon and make it stronger will be started after the bursitis has healed. You may gradually increase the amount of weight you put on your foot when caregivers say it is OK. You may be told to stop exercising if you feel any pain. Surgical Treatment Only if non-surgical attempts at treatment fail, will it make sense to consider surgery. Surgery for retrocalcanel bursitis can include many different procedures. Some of these include removal of the bursa, removing any excess bone at the back of the heel (calcaneal exostectomy), and occasionally detachment and re-attachment of the Achilles tendon. If the foot structure and shape of the heel bone is a primary cause of the bursitis, surgery to re-align the heel bone (calcaneal osteotomy) may be considered. Regardless of which exact surgery is planned, the goal is always to decrease pain and correct the deformity. The idea is to get you back to the activities that you really enjoy. Your foot and ankle surgeon will determine the exact surgical procedure that is most likely to correct the problem in your case. But if you have to have surgery, you can work together to develop a plan that will help assure success.  Overview OverviewA Hammer toe is a deformity of the second, third or fourth toe in which the toe becomes bent at the middle joint; hence, it resembles a hammer. Claw toe and mallet toe are related conditions. While a hammer toe is contracted at the first toe joint, a mallet toe is contracted at the second toe joint, and a claw toe is contracted at both joints. According to the 2012 National Foot Health Assessment conducted by the NPD Group for the Institute for Preventive Foot Health, 3 percent of U.S. adults age 21 and older (about 7 million people) have experienced hammer toe or claw toe. The condition is significantly more prevalent in females than in males. Causes Hammertoes are more commonly seen in women than men, due to the shoe styles women frequently wear: shoes with tight toe boxes and high heels. Genetics plays a role in some cases of hammertoes, as does trauma, infection, arthritis, and certain neurological and muscle disorders. But most cases of contracted toes are associated with various biomechanical abnormalities of the feet, such as flat feet and feet with abnormally high arches. These biomechanical abnormalities cause the muscles and tendons to be used excessively or improperly, which deforms the toes over time.  Symptoms SymptomsHammer toes can cause problems with walking and lead to other foot problems, such as blisters, calluses, and sores. Pain is caused by constant friction over the top of the toe?s main joint. It may be difficult to fit into some shoe gear due to the extra space required for the deformed toe. In many cases there will be pain on the ball of the foot over the metatarsals along with callus formation. This is due to the toes not functioning properly, failing to properly touch the ground during the gait cycle. The ball of the foot then takes the brunt of the ground forces, which causes chronic pain. Diagnosis The exam may reveal a toe in which the near bone of the toe (proximal phalanx) is angled upward and the middle bone of the toe points in the opposite direction (plantar flexed). Toes may appear crooked or rotated. The involved joint may be painful when moved, or stiff. There may be areas of thickened skin (corns or calluses) on top of or between the toes, a callus may also be observed at the tip of the affected toe beneath the toenail. An attempt to passively correct the deformity will help elucidate the best treatment option as the examiner determines whether the toe is still flexible or not. It is advisable to assess palpable pulses, since their presence is associated with a good prognosis for healing after surgery. X-rays will demonstrate the contractures of the involved joints, as well as possible arthritic changes and bone enlargements (exostoses, spurs). X-rays of the involved foot are usually performed in a weight-bearing position. Non Surgical Treatment In the early stages, the deformities from mallet toe, claw toe and hammertoe can be corrected. But if treatment is delayed too long, permanent stiffness can ensue which can only be corrected by surgery. The most effective treatment options are good fitting footwear. Shoes with a wide toebox will be more comfortable and will reduce the tension on the muscles and friction on the toes. Avoid high heels as they push your feet forwards to the front of the shoes. This increases the pressure on the toes, forcing them to bend more than usual. Shoes should ideally be half an inch longer than your longest toe. Exercises to strengthen and stretch the muscles can be really helpful. Simple things like trying to pick marbles up with your feet or scrunching up a towel underneath your foot can work well. Surgical Treatment There are several surgical methods to correct a hammer toe. Your physician will decide which method will be most beneficial to you depending on the severity of your deformity, the direction the toe is deviating and the length of the affected toe. Some common surgical methods include. Arthroplasty. To promote straightening, half of the joint located directly underneath the crooked part of the toe is removed. Arthrodesis (fusion) To promote straightening, the joint directly underneath where the toe is crooked is completely removed. A wire or pin is inserted to aid healing. Tendon transfer. Performed alone or in combination with other procedures, a surgeon will take tendons from under the toe and ?re-route? them to the top of the toe to promote straightening. Basal phalangectomy. Performed to assist patients with severe stiffness, this procedure removes the base of the bone underneath the toe. Weil osteotomy. Performed to assist patients with severe stiffness, this procedure involves shortening the metatarsal bone and inserting surgical hardware to aid healing. 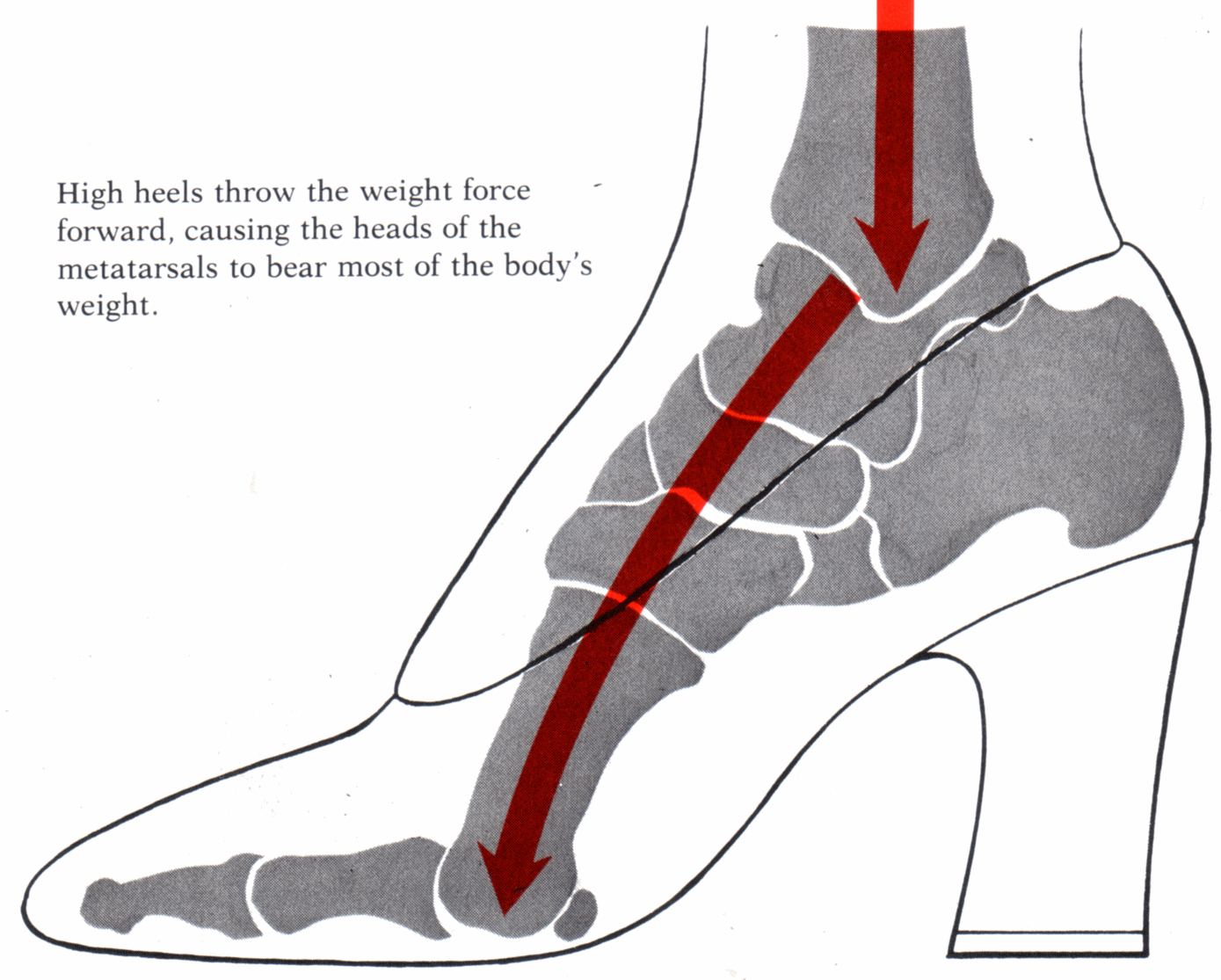 Prevention PreventionBe good to your feet, because they carry you. They are designed to last a lifetime, but that doesn?t mean they don?t need some love and care as well as some basic maintenance. Check your feet regularly for problems. This is especially true if you have diabetes or any other medical condition that causes poor circulation or numbness in your toes. If you do, check your feet every day so problems can be caught early on. Good circulation is essential. When you're sitting down, put your feet up. If hammertoe you've been sitting for a while, stretch your legs and feet. Give yourself a foot massage, or ask someone you love for a foot massage. A warm foot bath is also a good idea.
Overview
 Bunions are probably the most common foot disorder seen in podiatry. The term bunion itself is used by patients describing the bony lump found near the base of the big toe, which is usually an adaptation of the positional change of the big toe. Hallux abducto valgus (HAV) is a medical term, which describes the position of the hallux (big toe) with respect to the connecting bone of the mid foot (metatarsal). In this foot disorder, the hallux deviates towards the lesser toes and the metatarsal moves towards the midline. Bunions are probably the most common foot disorder seen in podiatry. The term bunion itself is used by patients describing the bony lump found near the base of the big toe, which is usually an adaptation of the positional change of the big toe. Hallux abducto valgus (HAV) is a medical term, which describes the position of the hallux (big toe) with respect to the connecting bone of the mid foot (metatarsal). In this foot disorder, the hallux deviates towards the lesser toes and the metatarsal moves towards the midline.Causes Contributing factors may include excessive foot pronation, wearing tight and pointed-toe shoes, and occasionally trauma. Joint misalignment causes osteoarthritis with cartilage erosion and exostosis formation, resulting in joint motion being limited (hallux limitus) or eliminated (hallux rigidus). In late stages, synovitis occurs, causing joint swelling. In reaction to pressure from tight shoes, an adventitious bursa can develop medial to the joint prominence, which can become painful, swollen, and inflamed. Symptoms Most patients complain of pain directly on the bunion area, within the big toe joint, and/or on the bottom of the foot. The bunion may become irritated, red, warm, swollen and/or callused. The pain may be dull and mild or severe and sharp. The size of the bunion doesn?t necessarily result in more pain. Pain is often made worse by shoes, especially shoes that crowd the toes. While some bunions may result in significant pain, other bunions may not be painful at all. Diagnosis A thorough medical history and physical exam by a physician is necessary for the proper diagnosis of bunions and other foot conditions. X-rays can help confirm the diagnosis by showing the bone displacement, joint swelling, and, in some cases, the overgrowth of bone that characterizes bunions. Doctors also will consider the possibility that the joint pain is caused by or complicated by Arthritis, which causes destruction of the cartilage of the joint. Gout, which causes the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joint. Tiny fractures of a bone in the foot or stress fractures. Infection. Your doctor may order additional tests to rule out these possibilities. Non Surgical Treatment Apply special pads and dressings to protect the bunion from shoe pressure. Inject steroid and local anesthetic around the bunion to reduce inflammation. This is especially useful if there is an associated bursitis. Recommend commercially available or custom made shoes. Prescribe functional orthotics to correct faulty foot function, and help prevent worsening of the deformity. Recommend bunion surgery to correct the deformity.  Surgical Treatment If non-surgical treatments have failed to relieve your bunion pain, or when the pain is interfering with your daily activities, contact the Dallas bunion surgery specialists at North Texas Foot & Ankle to discuss surgical options. There are a several ways to perform bunion surgery. The best procedure for one person is not necessarily the best for another. Some procedures allow you to walk much sooner, reducing the need for crutches. Depending on your foot type, the procedure can have a greater risk for return of the bunion deformity. Other procedures may require you to be on crutches for a few weeks - but could offer a better result in the long-term. Learn more about the different types of bunion surgery. Overview
One of the main postural deviations that cause pain and injury in the foot and ankle area (and resultant compensations in the rest of the body) is overpronation. Pronation is a normal function that occurs when the foot rolls inward toward the midline of the body. This movement causes the heel to collapse inward and the medial arch of the foot to elongate and flatten. Overpronation, however, is when the foot collapses too far inward for normal function. Consequently, this directly affects the ability of the foot to perform and can disrupt proper functioning through the entire body.  Causes There has been some speculation as to whether arch height has an effect on pronation. After conducting a study at the Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology, Maggie Boozer suggests that people with higher arches tend to pronate to a greater degree. However, the generally accepted view by professionals is that the most pronation is present in those with lower arch heights. To complicate matters, one study done by Hylton Menz at the University of Western Sydney-Macarthur suggests that the methods for measuring arch height and determining whether someone is ?flat-footed? or ?high-arched? are unreliable. He says, ?For this reason, studies investigating the relationship between static arch height motion of the rearfoot have consistently found that such a classification system is a poor predictor of dynamic rearfoot function. Symptoms Overpronation can be a contributing factor in other lower extremity disorders, such as foot pain, plantar fasciitis, ankle injuries, medial tibial stress syndrome (shin splints), periostitis, stress fractures and myofascial trigger points. Overpronation increases the degree of internal tibial rotation, thereby contributing to various knee disorders such as meniscal injury or ligament sprains. The effects of the postural deviation are exaggerated in athletes due to the increase in foot strikes while running and the greater impact load experienced. When running, three to four times the body weight is experienced with each foot strike.2 If overpronation exists, the shock force is not adequately absorbed by the foot and is transmitted further up the kinetic chain. Diagnosis If you have flat feet or low arches, chances are you overpronate. Although not always the case, the lower your arches the greater the overpronate. Stand on a hard surface (in front of a mirror if you need to) and look at your feet, flat feet or low arches are easy to spot. If your feet look flatter than a pancake, have a look at your ankles and see if they seem collapsed or straight. If they are, you're overpronating.  Non Surgical Treatment Your podiatrist will look at your current footwear to ensure that it is both well-fitted and possessed of adequate cushioning to protect your feet. Firm heel support is advised for over-pronators, and a good fit is important to ensure that the foot as a whole is well supported as instability can exacerbate the existing problems caused by over-pronation. Prevention Wear supportive shoes. If we're talking runners you're going to fall in the camp of needing 'motion control' shoes or shoes built for 'moderate' or 'severe' pronators. There are many good brands of shoes out there. Don't just wear these running, the more often the better. Make slow changes. Sudden changes in your training will aggravate your feet more than typical. Make sure you slowly increase your running/walking distance, speed and even how often you go per week. Strengthen your feet. As part of your running/walking warm up or just as part of a nightly routine try a few simple exercises to strengthen your feet, start with just ten of each and slowly add more sets and intensity. Stand facing a mirror and practice raising your arch higher off the ground without lifting your toes. Sit with a towel under your feet, scrunch your toes and try to pull the towel in under your feet. Sitting again with feet on the ground lift your heels as high as you can, then raise and lower on to toe tips. Overview
Sever?s disease occurs in children when the growing part of the heel is injured. This growing part is called the growth plate. The foot is one of the first body parts to grow to full size. This usually occurs in early puberty. During this time, bones often grow faster than muscles and tendons. As a result, muscles and tendons become ?tight.? The heel area is less flexible. During weight-bearing activity (activity performed while standing), the tight heel tendons may put too much pressure at the back of the heel (where the Achilles tendon attaches). This may injure the heel. Causes During the growth spurt of early puberty, the bones often grow faster than the leg muscles and tendons. This can cause the muscles to become very tight and overstretched, the heel becomes less flexible and this build-up of pressure can result in redness, swelling, tenderness and pain at the heel. Symptoms In Sever?s disease, heel pain can be in one or both heels. It usually starts after a child begins a new sports season or a new sport. Your child may walk with a limp. The pain may increase when he or she stands on tiptoe. Your child?s heel may hurt if you squeeze both sides toward the very back. This is called the squeeze test. Your provider may also find that your child?s heel tendons have become tight. Diagnosis The x-ray appearance usually shows the apophysis to be divided into multiple parts. Sometimes a series of small fragments is noted. Asymptomatic heels may also show x-ray findings of resporption, fragmentation and increased density. But they occur much less often in the normal foot. Pulling or ?traction? of the Achilles tendon on the unossified growth plate is a likely contributing factor to Sever?s disease. Excessive pronation and a tight Achilles and limited dorsiflexion may also contribute to the development of this condition. Non Surgical Treatment First, your child should cut down or stop any activity that causes heel pain. Apply ice to the injured heel for 20 minutes 3 times a day. If your child has a high arch, flat feet or bowed legs, your doctor may recommend orthotics, arch supports or heel cups. Your child should never go barefoot. If your child has severe heel pain, medicines such as acetaminophen (one brand name: Tylenol) or ibuprofen (some brand names: Advil, Motrin, Nuprin) may help. Surgical Treatment The surgeon may select one or more of the following options to treat calcaneal apophysitis. Reduce activity. The child needs to reduce or stop any activity that causes pain. Support the heel. Temporary shoe inserts or custom orthotic devices may provide support for the heel. Medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, help reduce the pain and inflammation. Physical therapy. Stretching or physical therapy modalities are sometimes used to promote healing of the inflamed issue. Immobilization. In some severe cases of pediatric heel pain, a cast may be used to promote healing while keeping the foot and ankle totally immobile. Often heel pain in children returns after it has been treated because the heel bone is still growing. Recurrence of heel pain may be a sign of calcaneal apophysitis, or it may indicate a different problem. If your child has a repeat bout of heel pain, be sure to make an appointment with your foot and ankle surgeon.
Overview Many foot problems can be contributed to Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity (AAFD), a foot and ankle condition that causes fallen arch of the foot. AAFD is also referred to as Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD). The posterior tibial tendon serves as the principal supporting structure of your foot. When this ligament is injured overtime the arches start to flatten, leaving you with a painful foot condition. AAFD is more common in women ages 39 - 65 than men.
 Causes Causes of an adult acquired flatfoot may include Neuropathic foot (Charcot foot) secondary to Diabetes mellitus, Leprosy, Profound peripheral neuritis of any cause. Degenerative changes in the ankle, talonavicular or tarsometatarsal joints, or both, secondary to Inflammatory arthropathy, Osteoarthropathy, Fractures, Acquired flatfoot resulting from loss of the supporting structures of the medial longitudinal arch. Dysfunction of the tibialis posterior tendon Tear of the spring (calcaneoanvicular) ligament (rare). Tibialis anterior rupture (rare). Painful flatfoot can have other causes, such as tarsal coalition, but as such a patient will not present with a change in the shape of the foot these are not included here. Symptoms In many cases, adult flatfoot causes no pain or problems. In others, pain may be severe. Many people experience aching pain in the heel and arch and swelling along the inner side of the foot. Diagnosis Although you can do the "wet test" at home, a thorough examination by a doctor will be needed to identify why the flatfoot developed. Possible causes include a congenital abnormality, a bone fracture or dislocation, a torn or stretched tendon, arthritis or neurologic weakness. For example, an inability to rise up on your toes while standing on the affected foot may indicate damage to the posterior tibial tendon (PTT), which supports the heel and forms the arch. If "too many toes" show on the outside of your foot when the doctor views you from the rear, your shinbone (tibia) may be sliding off the anklebone (talus), another indicator of damage to the PTT. Be sure to wear your regular shoes to the examination. An irregular wear pattern on the bottom of the shoe is another indicator of acquired adult flatfoot. Your physician may request X-rays to see how the bones of your feet are aligned. Muscle and tendon strength are tested by asking you to move the foot while the doctor holds it. Non surgical Treatment Medical or nonoperative therapy for posterior tibial tendon dysfunction involves rest, immobilization, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication, physical therapy, orthotics, and bracing. This treatment is especially attractive for patients who are elderly, who place low demands on the tendon, and who may have underlying medical problems that preclude operative intervention. During stage 1 posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, pain, rather than deformity, predominates. Cast immobilization is indicated for acute tenosynovitis of the posterior tibial tendon or for patients whose main presenting feature is chronic pain along the tendon sheath. A well-molded short leg walking cast or removable cast boot should be used for 6-8 weeks. Weight bearing is permitted if the patient is able to ambulate without pain. If improvement is noted, the patient then may be placed in custom full-length semirigid orthotics. The patient may then be referred to physical therapy for stretching of the Achilles tendon and strengthening of the posterior tibial tendon. Steroid injection into the posterior tibial tendon sheath is not recommended due to the possibility of causing a tendon rupture. In stage 2 dysfunction, a painful flexible deformity develops, and more control of hindfoot motion is required. In these cases, a rigid University of California at Berkley (UCBL) orthosis or short articulated ankle-foot orthosis (AFO) is indicated. Once a rigid flatfoot deformity develops, as in stage 3 or 4, bracing is extended above the ankle with a molded AFO, double upright brace, or patellar-tendon-bearing brace. The goals of this treatment are to accommodate the deformity, prevent or slow further collapse, and improve walking ability by transferring load to the proximal leg away from the collapsed medial midfoot and heel. Causes Causes of an adult acquired flatfoot may include Neuropathic foot (Charcot foot) secondary to Diabetes mellitus, Leprosy, Profound peripheral neuritis of any cause. Degenerative changes in the ankle, talonavicular or tarsometatarsal joints, or both, secondary to Inflammatory arthropathy, Osteoarthropathy, Fractures, Acquired flatfoot resulting from loss of the supporting structures of the medial longitudinal arch. Dysfunction of the tibialis posterior tendon Tear of the spring (calcaneoanvicular) ligament (rare). Tibialis anterior rupture (rare). Painful flatfoot can have other causes, such as tarsal coalition, but as such a patient will not present with a change in the shape of the foot these are not included here. Symptoms In many cases, adult flatfoot causes no pain or problems. In others, pain may be severe. Many people experience aching pain in the heel and arch and swelling along the inner side of the foot. Diagnosis Although you can do the "wet test" at home, a thorough examination by a doctor will be needed to identify why the flatfoot developed. Possible causes include a congenital abnormality, a bone fracture or dislocation, a torn or stretched tendon, arthritis or neurologic weakness. For example, an inability to rise up on your toes while standing on the affected foot may indicate damage to the posterior tibial tendon (PTT), which supports the heel and forms the arch. If "too many toes" show on the outside of your foot when the doctor views you from the rear, your shinbone (tibia) may be sliding off the anklebone (talus), another indicator of damage to the PTT. Be sure to wear your regular shoes to the examination. An irregular wear pattern on the bottom of the shoe is another indicator of acquired adult flatfoot. Your physician may request X-rays to see how the bones of your feet are aligned. Muscle and tendon strength are tested by asking you to move the foot while the doctor holds it. Non surgical Treatment Medical or nonoperative therapy for posterior tibial tendon dysfunction involves rest, immobilization, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication, physical therapy, orthotics, and bracing. This treatment is especially attractive for patients who are elderly, who place low demands on the tendon, and who may have underlying medical problems that preclude operative intervention. During stage 1 posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, pain, rather than deformity, predominates. Cast immobilization is indicated for acute tenosynovitis of the posterior tibial tendon or for patients whose main presenting feature is chronic pain along the tendon sheath. A well-molded short leg walking cast or removable cast boot should be used for 6-8 weeks. Weight bearing is permitted if the patient is able to ambulate without pain. If improvement is noted, the patient then may be placed in custom full-length semirigid orthotics. The patient may then be referred to physical therapy for stretching of the Achilles tendon and strengthening of the posterior tibial tendon. Steroid injection into the posterior tibial tendon sheath is not recommended due to the possibility of causing a tendon rupture. In stage 2 dysfunction, a painful flexible deformity develops, and more control of hindfoot motion is required. In these cases, a rigid University of California at Berkley (UCBL) orthosis or short articulated ankle-foot orthosis (AFO) is indicated. Once a rigid flatfoot deformity develops, as in stage 3 or 4, bracing is extended above the ankle with a molded AFO, double upright brace, or patellar-tendon-bearing brace. The goals of this treatment are to accommodate the deformity, prevent or slow further collapse, and improve walking ability by transferring load to the proximal leg away from the collapsed medial midfoot and heel.  Surgical Treatment Stage two deformities are less responsive to conservative therapies that can be effective in mild deformities. Bone procedures are necessary at this stage in order to recreate the arch and stabilize the foot. These procedures include isolated fusion procedures, bone grafts, and/or the repositioning of bones through cuts called osteotomies. The realigned bones are generally held in place with screws, pins, plates, or staples while the bone heals. A tendon transfer may or may not be utilized depending on the condition of the posterior tibial tendon. Stage three deformities are better treated with surgical correction, in healthy patients. Patients that are unable to tolerate surgery or the prolonged healing period are better served with either arch supports known as orthotics or bracing such as the Richie Brace. Surgical correction at this stage usually requires fusion procedures such as a triple or double arthrodesis. This involves fusing the two or three major bones in the back of the foot together with screws or pins. The most common joints fused together are the subtalar joint, talonavicular joint, and the calcaneocuboid joint. By fusing the bones together the surgeon is able to correct structural deformity and alleviate arthritic pain. Tendon transfer procedures are usually not beneficial at this stage. Stage four deformities are treated similarly but with the addition of fusing the ankle joint. Surgical Treatment Stage two deformities are less responsive to conservative therapies that can be effective in mild deformities. Bone procedures are necessary at this stage in order to recreate the arch and stabilize the foot. These procedures include isolated fusion procedures, bone grafts, and/or the repositioning of bones through cuts called osteotomies. The realigned bones are generally held in place with screws, pins, plates, or staples while the bone heals. A tendon transfer may or may not be utilized depending on the condition of the posterior tibial tendon. Stage three deformities are better treated with surgical correction, in healthy patients. Patients that are unable to tolerate surgery or the prolonged healing period are better served with either arch supports known as orthotics or bracing such as the Richie Brace. Surgical correction at this stage usually requires fusion procedures such as a triple or double arthrodesis. This involves fusing the two or three major bones in the back of the foot together with screws or pins. The most common joints fused together are the subtalar joint, talonavicular joint, and the calcaneocuboid joint. By fusing the bones together the surgeon is able to correct structural deformity and alleviate arthritic pain. Tendon transfer procedures are usually not beneficial at this stage. Stage four deformities are treated similarly but with the addition of fusing the ankle joint.
Overview
The sensation of sore, aching feet or arch pain refers to an inflammation and burning sensation at the arch of the foot. This inflammation is due to the excessive stretching of the fibrous tissue located along the bottom surface of the foot, called plantar fascia. Plantar fascitis is the term named after this condition and described as inflammation of the fascia, muscles and ligaments on the bottom of the foot, causing pain in the heel and arch of the foot.  Causes Also known as pes planus, this is when the arch of the foot collapses completely dropping the whole sole of the foot down to the ground. Flat feet are a common cause of foot arch pain. Babies are born with flat feet and as they grow, the foot arches should gradually form, but in approximately 30% of the population, they never do. They can also develop later in life, due to illness, pregnancy, injury, excessive stress on the feet or as part of the aging process. Many people who have flat feet don?t complain of any accompanying symptoms, but some develop foot arch pain, or problems further up the leg such as knee pain or back pain. They may find their feet tire quickly when they are standing or walking, and that it is difficult to rise up onto their tiptoes. Someone who is experiencing pain on the bottom of the foot or elsewhere due to their flat feet can benefit from exercises and orthotics (specially designed insoles to correct the foot position) as well as walking barefoot rather than in shoes. A quick test to see if you have flat feet is to put your foot in a tray of water and then place it on a smooth level surface e.g. thick paper. Have a look at your footprint, the more of the sole of the foot that you can see, the flatter your foot. Symptoms The most common symptoms of plantar fasciitis include pain on the bottom of the foot near the heel, pain with the first few steps after getting out of bed in the morning, or after a long period of rest, such as after a long car ride. The pain subsides after a few minutes of walking. Greater pain after (not during) exercise or activity. Diagnosis The diagnosis of high arch (cavus) foot deformity or Charcot Marie Tooth disease can be made by an orthopedic surgeon in the office. Evaluation includes a thorough history and physical examination as well as imaging studies such as X-rays. The orthopedic surgeon will look at the overall shape, flexibility, and strength of a patient?s foot and ankle to help determine the best treatment. Nerve tests may occasionally need to be performed to help confirm the diagnosis. Non Surgical Treatment Tight arches, overpronation and flat feet as well as tight calves all lead to inflammation of the connective tissue that forms this arch of your foot. This condition, plantar fasciitis, can be very painful, from your first step in the morning. Fortunately, treatment is easier than most. No operations, no fancy pulsed waves, no night splints necessary. Good arch supports? full length flexible (not hard) orthotics are key. Stretches of the calf relieve arch tightness as the heel bone acts like a fulcrum pulling back the arch tissues if too tight. Regularly perform the gastroc and soleus stretches that you learned at the gym. If lazy, buy "Pro-Stretch" on line which helps you stretch your calves easily. Use it often. You can't stretch too often, only too little. Finally, the magic cure is to roll a golf ball under the arch for half-hour once a day. (I know; a half-hour is a long time to perform one exercise, but that's what it takes. Once you master this exercise, it is easy to do while you work at your desk or are watching a half hour TV program.) This may hurt the first week. Keep going because by week two, after you go over the pain hump, the pain will be gone.  Surgical Treatment As with most surgeries, patients and physicians should consider the surgery only after other, less invasive treatments have proven unproductive. Indications for surgery include Pain. Inability to function. Failure to improve after a six-month course of specific, directed physical therapy. Failure to improve after using arch supports, orthotics, or ankle and foot bracing. Once patients are at that point, the good news is that the procedure has considerably better outcomes than more traditional flat foot surgery. In the past, surgeons would realign and fuse the three hind joints, which would cause patients to lose motion, leaving them with a significantly stiff hind foot, With these newer procedures, if the foot is still flexible, surgeons can realign it and usually restore a close-to-normal or functional range of motion in the joints. Stretching Exercises You may start exercising the muscles of your foot right away by gently stretching and strengthening them. Frozen can roll. Roll your bare injured foot back and forth from your heel to your mid-arch over a frozen juice can. Repeat for 3 to 5 minutes. This exercise is particularly helpful if it is done first thing in the morning. Towel stretch. Sit on a hard surface with your injured leg stretched out in front of you. Loop a towel around your toes and the ball of your foot and pull the towel toward your body keeping your leg straight. Hold this position for 15 to 30 seconds and then relax. Repeat 3 times. Standing calf stretch. Stand facing a wall with your hands on the wall at about eye level. Keep your injured leg back with your heel on the floor. Keep the other leg forward with the knee bent. Turn your back foot slightly inward (as if you were pigeon-toed). Slowly lean into the wall until you feel a stretch in the back of your calf. Hold the stretch for 15 to 30 seconds. Return to the starting position. Repeat 3 times. Do this exercise several times each day. Seated plantar fascia stretch. Sit in a chair and cross the injured foot over the knee of your other leg. Place your fingers over the base of your toes and pull them back toward your shin until you feel a comfortable stretch in the arch of your foot. Hold 15 seconds and repeat 3 times. Plantar fascia massage. Sit in a chair and cross the injured foot over the knee of your other leg. Place your fingers over the base of the toes of your injured foot and pull your toes toward your shin until you feel a stretch in the arch of your foot. With your other hand, massage the bottom of your foot, moving from the heel toward your toes. Do this for 3 to 5 minutes. Start gently. Press harder on the bottom of your foot as you become able to tolerate more pressure.
Overview
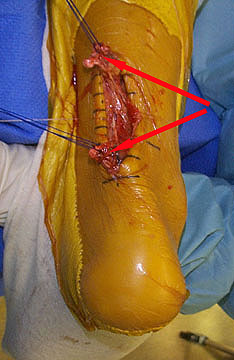 Achilles tendon rupture are common. Most athletes describe a sudden acute event with an associated popping sensation and pain in the Achilles tendon. They often think that they have been kicked or struck in the calf. It is important to get prompt treatment and to be placed in an equinous cast (a cast with the foot in a pointed position). More definitive treatment options can be discussed after this has occurred. Causes The most common cause of a ruptured Achilles' tendon is when too much stress is placed through the tendon, particularly when pushing off with the foot. This may happen when playing sports such as football, basketball or tennis where the foot is dorsiflexed or pushed into an upward position during a fall. If the Achilles' tendon is weak, it is prone to rupture. Various factors can cause weakness, including corticosteroid medication and injections, certain diseases caused by hormone imbalance and tendonitis. Old age can also increase the risk of Achilles' tendon rupture. Symptoms Patients present with acute posterior ankle/heel pain and may give a history of ?felt like someone kicked me from behind?. Patients may report a direct injury, or report the pain started with jumping or landing on a dorsiflexed foot. It is important to elicit in the history any recent steroid or flouroqunolone usage including local steroid injections, and also any history of endocrine disorders or systemic inflammatory conditions. Diagnosis The actual area of an Achilles tendon rupture cannot be seen on x-ray. Therefore, although x-rays are often done to rule out bony injuries in individuals with an Achilles tendon rupture these x-rays are usually normal. Diagnostic ultrasound of the tendon can be performed to assess the integrity of the tendon. Other diagnostic tests, such as MRI's, may also be required in difficult cases. Non Surgical Treatment A medical professional will take MRI scans to confirm the diagnosis and indicate the extent of the injury. Sometimes the leg is put in a cast and allowed to heal without surgery. This is generally not the preferred method, particularly for young active people. Surgery is the most common treatment for an achilles tendon rupture. Achilles tendon rupture are common. Most athletes describe a sudden acute event with an associated popping sensation and pain in the Achilles tendon. They often think that they have been kicked or struck in the calf. It is important to get prompt treatment and to be placed in an equinous cast (a cast with the foot in a pointed position). More definitive treatment options can be discussed after this has occurred. Causes The most common cause of a ruptured Achilles' tendon is when too much stress is placed through the tendon, particularly when pushing off with the foot. This may happen when playing sports such as football, basketball or tennis where the foot is dorsiflexed or pushed into an upward position during a fall. If the Achilles' tendon is weak, it is prone to rupture. Various factors can cause weakness, including corticosteroid medication and injections, certain diseases caused by hormone imbalance and tendonitis. Old age can also increase the risk of Achilles' tendon rupture. Symptoms Patients present with acute posterior ankle/heel pain and may give a history of ?felt like someone kicked me from behind?. Patients may report a direct injury, or report the pain started with jumping or landing on a dorsiflexed foot. It is important to elicit in the history any recent steroid or flouroqunolone usage including local steroid injections, and also any history of endocrine disorders or systemic inflammatory conditions. Diagnosis The actual area of an Achilles tendon rupture cannot be seen on x-ray. Therefore, although x-rays are often done to rule out bony injuries in individuals with an Achilles tendon rupture these x-rays are usually normal. Diagnostic ultrasound of the tendon can be performed to assess the integrity of the tendon. Other diagnostic tests, such as MRI's, may also be required in difficult cases. Non Surgical Treatment A medical professional will take MRI scans to confirm the diagnosis and indicate the extent of the injury. Sometimes the leg is put in a cast and allowed to heal without surgery. This is generally not the preferred method, particularly for young active people. Surgery is the most common treatment for an achilles tendon rupture.  Surgical Treatment There are two different types of surgeries; open surgery and percutaneous surgery. During an open surgery an incision is made in the back of the leg and the Achilles tendon is stitched together. In a complete or serious rupture the tendon of plantaris or another vestigial muscle is harvested and wrapped around the Achilles tendon, increasing the strength of the repaired tendon. If the tissue quality is poor, e.g. the injury has been neglected, the surgeon might use a reinforcement mesh (collagen, Artelon or other degradable material). In percutaneous surgery, the surgeon makes several small incisions, rather than one large incision, and sews the tendon back together through the incision(s). Surgery may be delayed for about a week after the rupture to let the swelling go down. For sedentary patients and those who have vasculopathy or risks for poor healing, percutaneous surgical repair may be a better treatment choice than open surgical repair. Surgical Treatment There are two different types of surgeries; open surgery and percutaneous surgery. During an open surgery an incision is made in the back of the leg and the Achilles tendon is stitched together. In a complete or serious rupture the tendon of plantaris or another vestigial muscle is harvested and wrapped around the Achilles tendon, increasing the strength of the repaired tendon. If the tissue quality is poor, e.g. the injury has been neglected, the surgeon might use a reinforcement mesh (collagen, Artelon or other degradable material). In percutaneous surgery, the surgeon makes several small incisions, rather than one large incision, and sews the tendon back together through the incision(s). Surgery may be delayed for about a week after the rupture to let the swelling go down. For sedentary patients and those who have vasculopathy or risks for poor healing, percutaneous surgical repair may be a better treatment choice than open surgical repair.
Overview
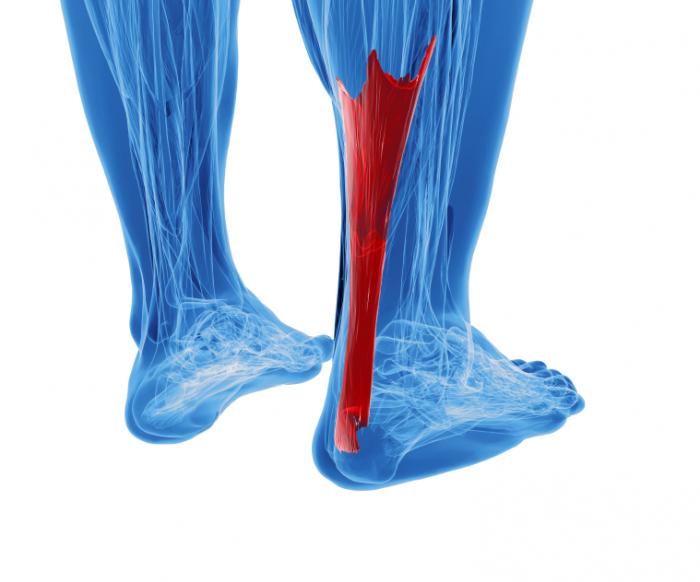 An Achilles tendon rupture is when part or all of your tendon is torn. The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscle in your lower leg to your heel bone. It allows you to point your foot down and to rise on your toes. A tear is caused by an injury or increased pressure, such as during sports or a fall. The following may make your Achilles tendon weak or stiff, and more likely to tear. A past tendon tear. Lack of physical activity. Abnormal bone structure in your foot. Obesity. Older age. Medicines, such as steroids and antibiotics. Causes The tendon is susceptible to injury and can rupture during vigorous activities such as running and jumping. Rupture can also occur as a result of gradual wear. After becoming chronically weakened, it can rupture during non-stress activities like walking. Symptoms Whereas calf strains and tendonitis may cause tightness or pain in the leg, Achilles tendon ruptures are typically accompanied by a popping sensation and noise at the time of the injury. In fact, some patients joke that the popping sound was loud enough to make them think they?d been shot. Seeing a board-certified orthopedic surgeon is the best way to determine whether you have suffered an Achilles tendon tear. Diagnosis On physical examination the area will appear swollen and ecchymotic, which may inhibit the examiners ability to detect a palpable defect. The patient will be unable to perform a single heel raise. To detect the presence of a complete rupture the Thompson test can be performed. The test is done by placing the patient prone on the examination table with the knee flexed to 90?, which allows gravity and the resting tension of the triceps surae to increase the dorsiflexion at the ankle. The calf muscle is squeezed by the examiner and a lack of planar flexion is noted in positive cases. It is important to note that active plantar flexion may still be present in the face of a complete rupture due to the secondary flexor muscles of the foot. It has been reported that up to 25% of patients may initially be missed in the emergency department due to presence of active plantar flexion and swelling over the Achilles tendon, which makes palpation of a defect difficult. Non Surgical Treatment Achilles tendon rupture is treated using non surgical method or surgical method. Non surgical treatment involves wearing a cast or special brace which is changed after some period of time to bring the tendon back to its normal length. Along with cast or brace, physical therapy may be recommended to improve the strength and flexibility of leg muscles and Achilles tendon. An Achilles tendon rupture is when part or all of your tendon is torn. The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscle in your lower leg to your heel bone. It allows you to point your foot down and to rise on your toes. A tear is caused by an injury or increased pressure, such as during sports or a fall. The following may make your Achilles tendon weak or stiff, and more likely to tear. A past tendon tear. Lack of physical activity. Abnormal bone structure in your foot. Obesity. Older age. Medicines, such as steroids and antibiotics. Causes The tendon is susceptible to injury and can rupture during vigorous activities such as running and jumping. Rupture can also occur as a result of gradual wear. After becoming chronically weakened, it can rupture during non-stress activities like walking. Symptoms Whereas calf strains and tendonitis may cause tightness or pain in the leg, Achilles tendon ruptures are typically accompanied by a popping sensation and noise at the time of the injury. In fact, some patients joke that the popping sound was loud enough to make them think they?d been shot. Seeing a board-certified orthopedic surgeon is the best way to determine whether you have suffered an Achilles tendon tear. Diagnosis On physical examination the area will appear swollen and ecchymotic, which may inhibit the examiners ability to detect a palpable defect. The patient will be unable to perform a single heel raise. To detect the presence of a complete rupture the Thompson test can be performed. The test is done by placing the patient prone on the examination table with the knee flexed to 90?, which allows gravity and the resting tension of the triceps surae to increase the dorsiflexion at the ankle. The calf muscle is squeezed by the examiner and a lack of planar flexion is noted in positive cases. It is important to note that active plantar flexion may still be present in the face of a complete rupture due to the secondary flexor muscles of the foot. It has been reported that up to 25% of patients may initially be missed in the emergency department due to presence of active plantar flexion and swelling over the Achilles tendon, which makes palpation of a defect difficult. Non Surgical Treatment Achilles tendon rupture is treated using non surgical method or surgical method. Non surgical treatment involves wearing a cast or special brace which is changed after some period of time to bring the tendon back to its normal length. Along with cast or brace, physical therapy may be recommended to improve the strength and flexibility of leg muscles and Achilles tendon.  Surgical Treatment Surgery may be indicated directly following injury rather than conservative care. Repair of an achilles tendon rupture is greatly varied for each clinical situation. There may be a direct repair of the ends of the tendon with suture, or possibly a tendon graft used to augment the tendon. Post-operatively, the period of immobilization will depend on the size of the defect that was repaired and how it was completed. Usually the immobilization is between 6-10 weeks. This repair may allow for a complete return to normal function, but in many instances the healing is complicated with adhesions and a partial loss of range of motion. There may be a continued soft tissue defect noted and a permanent or prolonged swelling. Surgical Treatment Surgery may be indicated directly following injury rather than conservative care. Repair of an achilles tendon rupture is greatly varied for each clinical situation. There may be a direct repair of the ends of the tendon with suture, or possibly a tendon graft used to augment the tendon. Post-operatively, the period of immobilization will depend on the size of the defect that was repaired and how it was completed. Usually the immobilization is between 6-10 weeks. This repair may allow for a complete return to normal function, but in many instances the healing is complicated with adhesions and a partial loss of range of motion. There may be a continued soft tissue defect noted and a permanent or prolonged swelling.
Overview
 Complete Achilles tendon ruptures occur most commonly at the mid-substance, but also distally at the insertion site or proximally at the myotendinous junction. These can be traumatic and devastating injuries, resulting in significant pain, disability, and healthcare cost. As many as 2.5 million individuals sustain Achilles tendon ruptures each year and the incidence is rising. This trend is due, in part, to an increase in athletic participation across individuals of all ages. Complete Achilles tendon ruptures occur most commonly at the mid-substance, but also distally at the insertion site or proximally at the myotendinous junction. These can be traumatic and devastating injuries, resulting in significant pain, disability, and healthcare cost. As many as 2.5 million individuals sustain Achilles tendon ruptures each year and the incidence is rising. This trend is due, in part, to an increase in athletic participation across individuals of all ages.Causes Often the individual will feel or hear a pop or a snap when the injury occurs. There is immediate swelling and severe pain in the back of the heel, below the calf where it ruptures. Pain is usually severe enough that it is difficult or impossible to walk or take a step. The individual will not be able to push off or go on their toes. Symptoms You may notice the symptoms come on suddenly during a sporting activity or injury. You might hear a snap or feel a sudden sharp pain when the tendon is torn. The sharp pain usually settles quickly, although there may be some aching at the back of the lower leg. After the injury, the usual symptoms are as follows. A flat-footed type of walk. You can walk and bear weight, but cannot push off the ground properly on the side where the tendon is ruptured. Inability to stand on tiptoe. If the tendon is completely torn, you may feel a gap just above the back of the heel. However, if there is bruising then the swelling may disguise the gap. If you suspect an Achilles tendon rupture, it is best to see a doctor urgently, because the tendon heals better if treated sooner rather than later. Diagnosis Your doctor diagnoses the rupture based on symptoms, history of the injury and physical examination. Your doctor will gently squeeze the calf muscles, if the Achilles tendon is intact, there will be flexion movement of the foot, if it is ruptured, there will be no movement observed. Non Surgical Treatment If you suspect a total rupture of the achilles tendon then apply cold therapy and compression and seek medical attention as soon as possible. In most cases surgery is required and the sooner this takes place the higher the chances of success. If the injury is left longer than two days then the chances of a successful outcome decrease. Cold and compression can also be applied throughout the rehabilitation phase as swelling is likely to be an issue with such a serious injury.  Surgical Treatment The surgical repair of an acute or chronic rupture of the Achilles tendon typically occurs in an outpatient setting. This means the patient has surgery and goes home the same day. Numbing medicine is often placed into the leg around the nerves to help decrease pain after surgery. This is called a nerve block. Patients are then put to sleep and placed in a position that allows the surgeon access to the ruptured tendon. Repair of an acute rupture often takes somewhere between 30 minutes and one hour. Repair of a chronic rupture can take longer depending on the steps needed to fix the tendon. Prevention To prevent Achilles tendonitis or rupture, the following tips are recommended. Avoid activities that place an enormous stress on the heel (for example, uphill running or excessive jumping). Stop all activity if there is pain at the back of the heel. If pain resumes with one particular exercise, another exercise should be selected. Wear proper shoes. Gradually strengthen calf muscles with sit-ups if prior episodes of Achilles tendonitis have occurred. Always warm up with stretching exercises before any activity. Avoid high-impact sports if prior episodes of Achilles tendon injury. |
|
